Understanding the Interoperable, Scalable and Decentralized Ecosystem of Cosmos
by Russian Defi
Cosmos is an ecosystem of independent blockchains that provides a blueprint for designing application-specific blockchains called Zones. Currently, there are 49 Zones in the Cosmos ecosystem. These zones are blockchains that are connected to the Hub and have their own tokens and validator sets.
Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) allows for the connection between these blockchains, which is more than just a bridge. It is a general-purpose message-passing protocol that leverages the instant finality of Tendermint.
Since each Zone is powered by consensus algorithms with Tendermint, any chain with fast finality can be connected to the Hub and use IBC.
As we look ahead to blockchain and cryptocurrency in 2023, it’s important to remember why people, projects, and dApps are interested in the Cosmos blockchain.
Here are just a few reasons why dApps are moving to Cosmos:
1) Interoperability:
- One of the main goals of Cosmos is to create a decentralized network of independent blockchains that can communicate and exchange data with each other. This interoperability is important because it allows different blockchain projects to work together and exchange value, which could lead to new use cases and applications.
The Cosmos-SDK and Tendermint Core made blockchains faster and easier to build, while IBC makes them interoperable at a worldwide network scale.
2) Scalability:
- Another key feature of Cosmos is its ability to scale. The network uses a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, which is more efficient and requires less energy than proof-of-work algorithms. This means that the network can handle a higher volume of transactions and support a larger number of users.
- Also, the Cosmos ecosystem can achieve scalability through the use of horizontal scaling. It can handle an increased workload by simply adding more hardware resources rather than upgrading individual nodes. This allows the Cosmos ecosystem to scale out and handle a larger number of transactions and users as needed.
3) Decentralization:
- Cosmos is designed to be a decentralized network with no single point of failure. This decentralization makes it resistant to censorship and tampering, which is important for maintaining trust and security in the network.
4) Community-driven development:
- The Cosmos project is governed by the Cosmos community, which means that the direction of the project is largely driven by the needs and interests of its users. This community-driven approach ensures that the network is responsive to the needs of its users and that it evolves in a way that benefits the broader ecosystem.
Cosmos Partnerships
Cosmos has partnered with the Ethereum Foundation to develop the Ethereum-Cosmos (Eth-Cos) Interchain, which allows for the transfer of value and data between the Ethereum and Cosmos networks.
Cosmos has also partnered with the Interchain Foundation, a Swiss non-profit organization that aims to promote and support the development of decentralized networks and technologies, to develop the IBC protocol.
Other notable Cosmos partnerships include those with ChainGuardian, a security firm specializing in blockchain and smart contract security; ChainSafe Systems, a blockchain research and development company; and the Web3 Foundation, which supports the development of decentralized technologies and protocols.
Interesting projects building on Cosmos:
Many interesting projects are being built on the Cosmos blockchain. Some examples include:
GNO land: Concurrent Smart Contracts that scale by utilizing gnolang (fork of Golang).
Agoric: Layer 1, where developers can deploy smart contracts in Javascript.
dYdX: Decentralised perpetual exchange moving from Starkware.
Kujira: Layer 1 platform for community-selected projects creating true value.
Nomic: A layer 1 Non-Custodial Bridge that allows users to access $BTC on Cosmos. It’s important to note Nomic is still in testnet!
Stride: The first liquid staking chain to launch in the Cosmos, providing liquid staking for assets across the Cosmos ecosystem.
Sei: The first order book-specific L1 blockchain built using the Cosmos SDK and Tendermint core.
Quicksilver: A sovereign permissionless liquid staking zone built on the Cosmos SDK.
IRISnet: A business blockchain platform that is built on the Cosmos blockchain and designed for use in enterprise applications.
DeFund: The first blockchain allows you to combine your choice of hundreds of tokenized assets into exchange-traded portfolios.
Mars protocol: Enable Integration of all trading activity possible on a CEX.
Final Thoughts
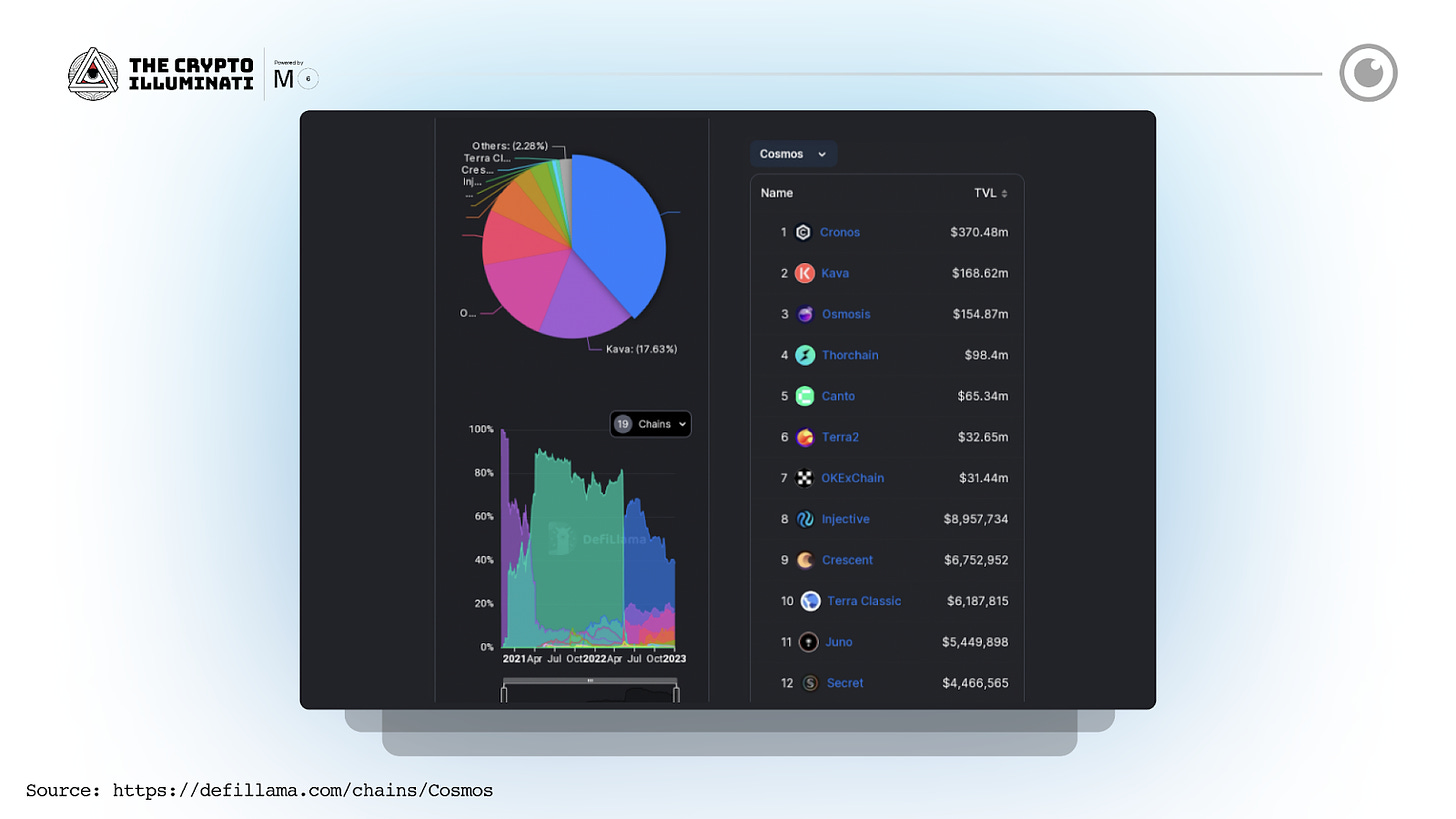
The Cosmos ecosystem is growing exponentially and is likely to continue doing so, making it an important player in the world of blockchain technology.
One of the key differences between Cosmos and other products is that it is an ecosystem of modular, adaptive, and replaceable tools. To make the promise of blockchain technology a reality, developers are invited to participate in enhancing current tools and developing new ones. The decentralized internet and future global financial system can only be built on top of these tools.
Whether you are a developer, investor, or simply someone interested in blockchain technology, Cosmos is an ecosystem worth paying attention to in 2023.