Foresight introduction to the thesis
What is node decentralisation, and why is it important in blockchain networks?
Node decentralisation refers to the distribution of nodes, or individual computers, that participate in a blockchain network. In other words, it is the degree to which a blockchain network is distributed across many different nodes rather than being controlled by a central authority. Node decentralisation is important in blockchain networks because it helps ensure security and prevent centralization, which can lead to vulnerabilities and potential manipulation of the network. Additionally, decentralisation can promote transparency and trust in the network by allowing for more participants to verify transactions and contribute to the consensus process.
How do the authors measure node decentralisation across multiple blockchain platforms?
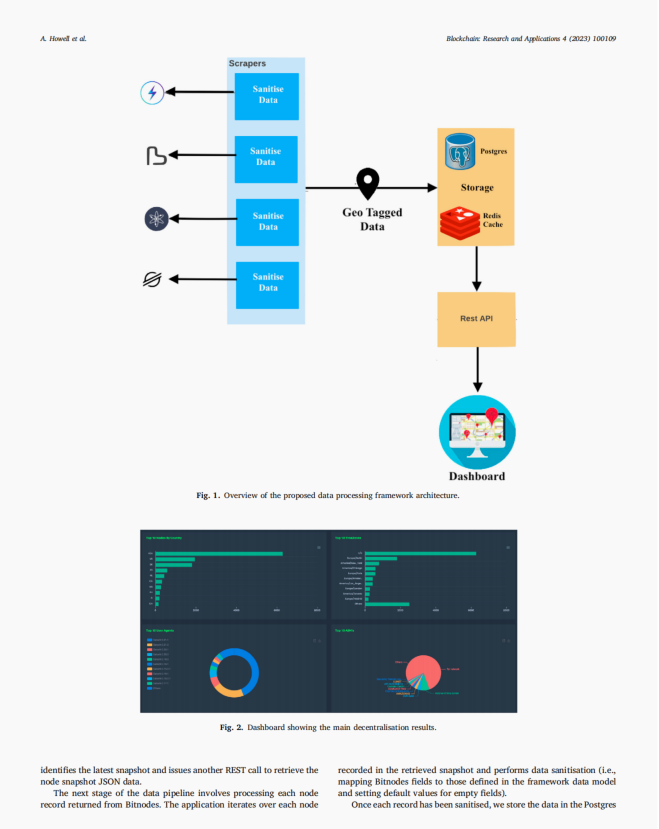
The authors propose a data processing framework called NodeMaps to capture, analyze, and visualize data from several popular peer-to-peer (P2P) blockchain platforms, including Cosmos, Stellar, Bitcoin, and Lightning Network. NodeMaps collects data on the geographic distribution of nodes, the diversity of hosting providers, and the variance in software clients used by nodes on each platform. The authors then use this data to calculate various metrics related to node decentralization, such as the Gini coefficient and Lorenz curve. By comparing and contrasting these metrics across multiple blockchain platforms, the authors aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of node decentralization in P2P blockchain networks.
What are some potential implications of low node decentralisation in blockchain networks?
Low node decentralization in blockchain networks can have several potential implications. Firstly, it can lead to a higher risk of centralization, which can make the network more vulnerable to attacks and manipulation. This is because a small number of nodes could potentially control the majority of the network’s computing power and decision-making processes. Secondly, low node decentralization can reduce transparency and trust in the network, as fewer participants are involved in verifying transactions and contributing to the consensus process. Finally, low node decentralization can limit the scalability of the network, as a small number of nodes may not be able to handle large volumes of transactions or data. Low node decentralization in blockchain networks can have several potential implications. Firstly, it can lead to a higher risk of centralization, which can make the network more vulnerable to attacks and manipulation. This is because a small number of nodes could potentially control the majority of the network’s computing power and decision-making processes. Secondly, low node decentralization can reduce transparency and trust in the network, as fewer participants are involved in verifying transactions and contributing to the consensus process. Finally, low node decentralization can limit the scalability of the network, as a small number of nodes may not be able to handle large volumes of transactions or data.