An overview of Ethereum performance across the protocol, DeFi, L2s and NFTs.
With 2022 now a couple weeks in the rearview mirror, we’re taking some time to reflect on the fiscal performance of the Ethereum blockchain in the last three months of the year. These numbers compare performance from Q4 2022 to Q4 2021.
(This piece was originally inspired by “Ethereum Announces First Quarter 2021 Results” by James Wang)
by Ben Giove, Bankless Analyst
Key Results
👨💻Protocol
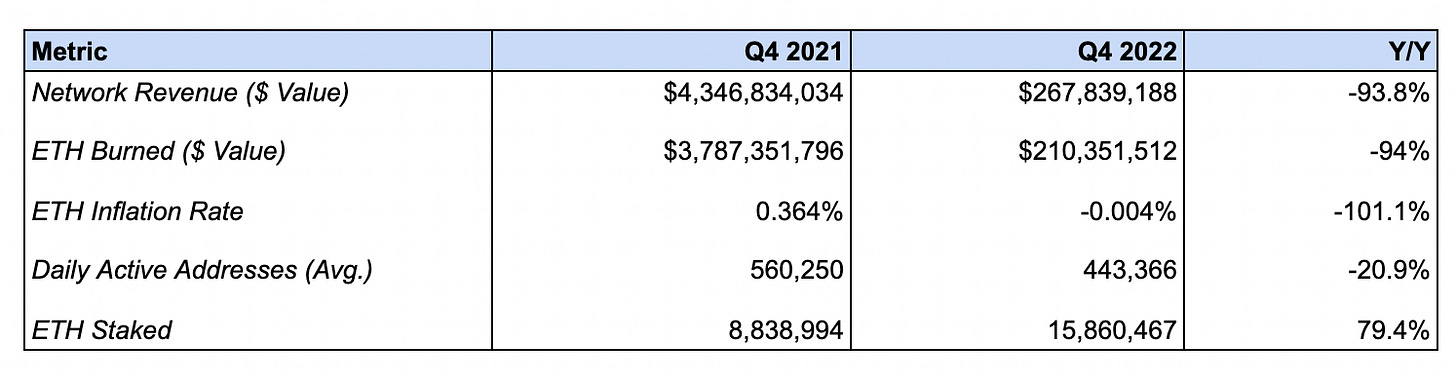
Network revenue dropped -93.8% from $4.3B to $267.8M. The USD value of ETH burned fell -94% from $3.8B to $210.4M
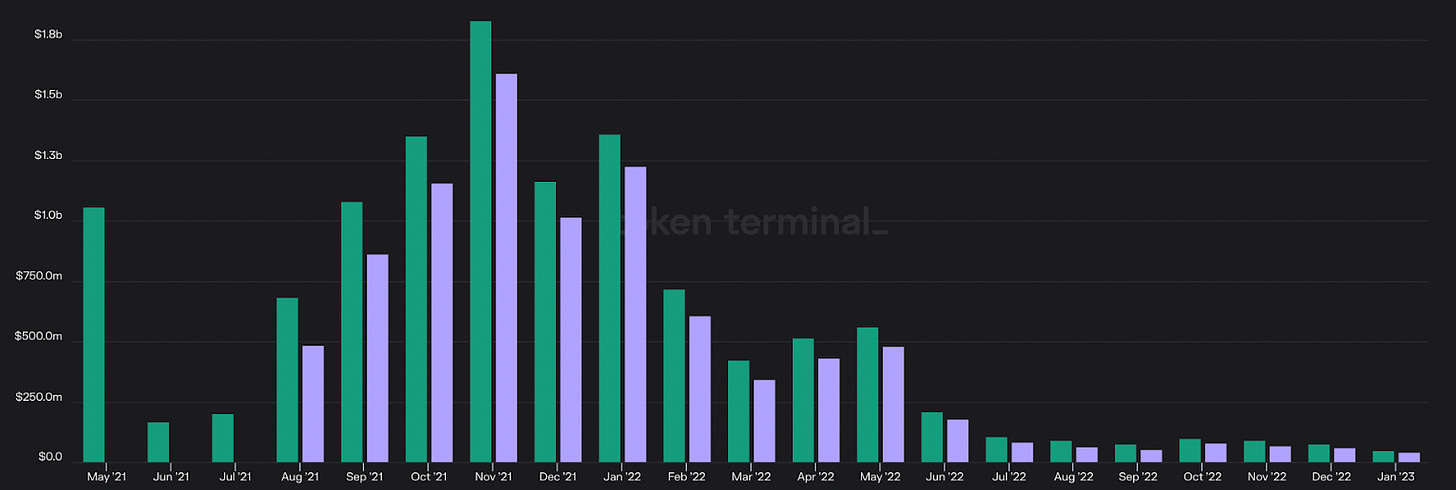
Network revenues measure the value of transaction fees paid by users to validators as well as the portion of said fees which is burned (i.e. removed from the circulating supply of ETH).
This decline is the result of falling crypto prices. Given that most on-chain activity today revolves around use-cases that are closely correlated to market cycles, such as ERC-20 and NFT trading, depressed prices led to a decrease in trading activity and therefore blockspace demand. The fall in the price of ETH, in which network revenue is denominated, has also contributed to this decrease.
The ETH inflation rate decreased -101.1% from 0.364% to -0.004%
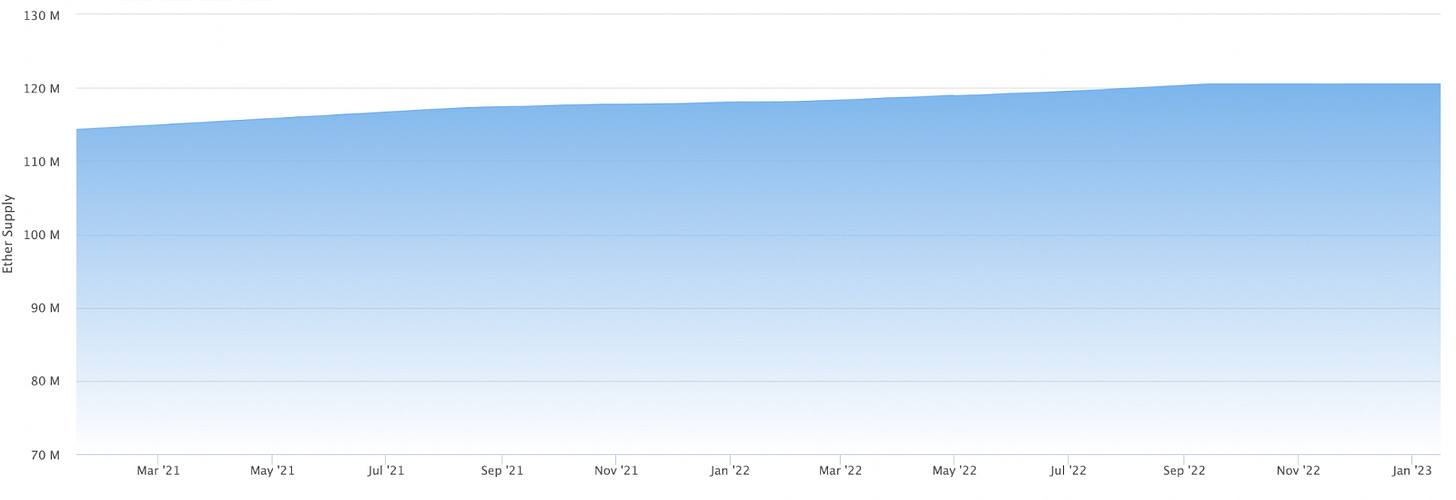
This metric measures the growth in the supply of ETH over the course of the quarter. The decline in issuance can be attributed to the reduction in emissions following Ethereum’s transition to Proof-of-Stake, which was completed in Q3. As a result, the ETH supply was net-deflationary in Q4. 🦇🔊
🏦 DeFi Ecosystem
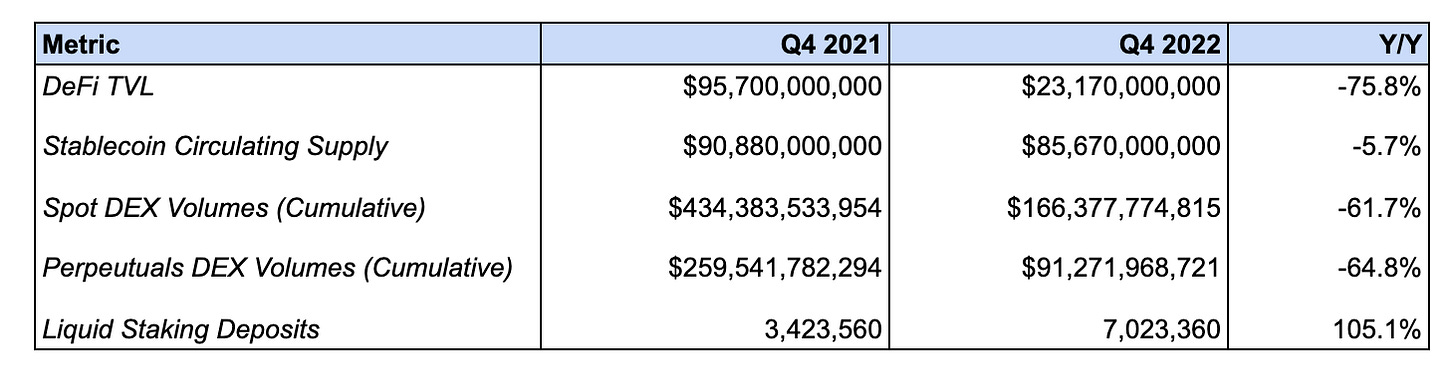
DeFi TVL fell -75.8% from $95.7B to $23.2B
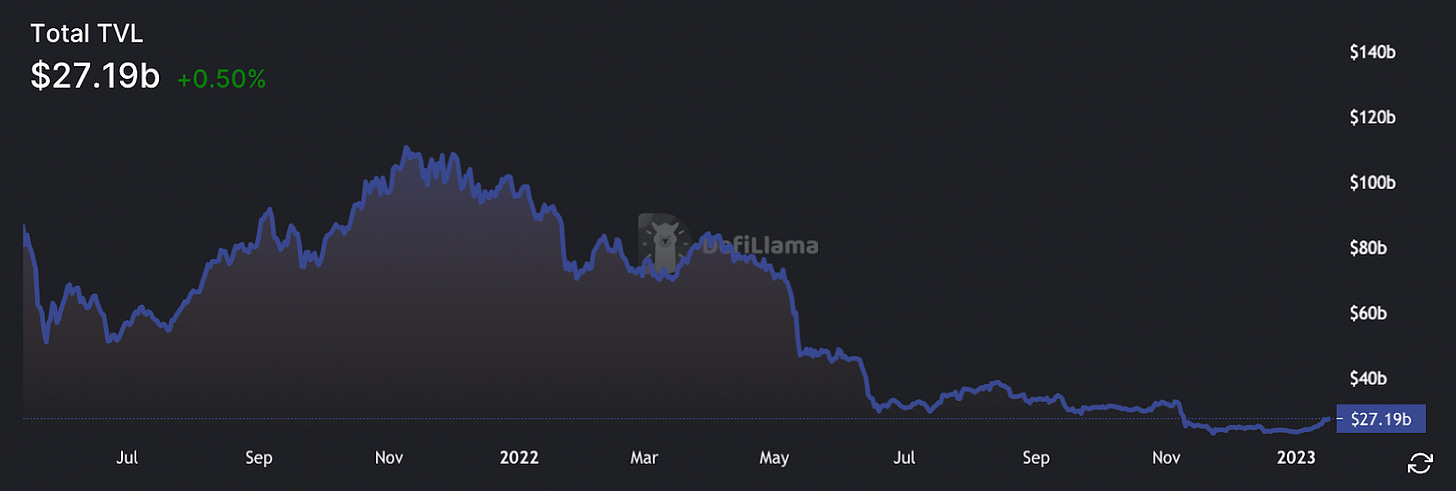
This decline is due to the decrease in broader crypto prices, which had fallen considerably by Q4 ‘22 relative to Q4 ‘21.
The stablecoin circulating supply fell -5.7% from $90.8B to $85.7B
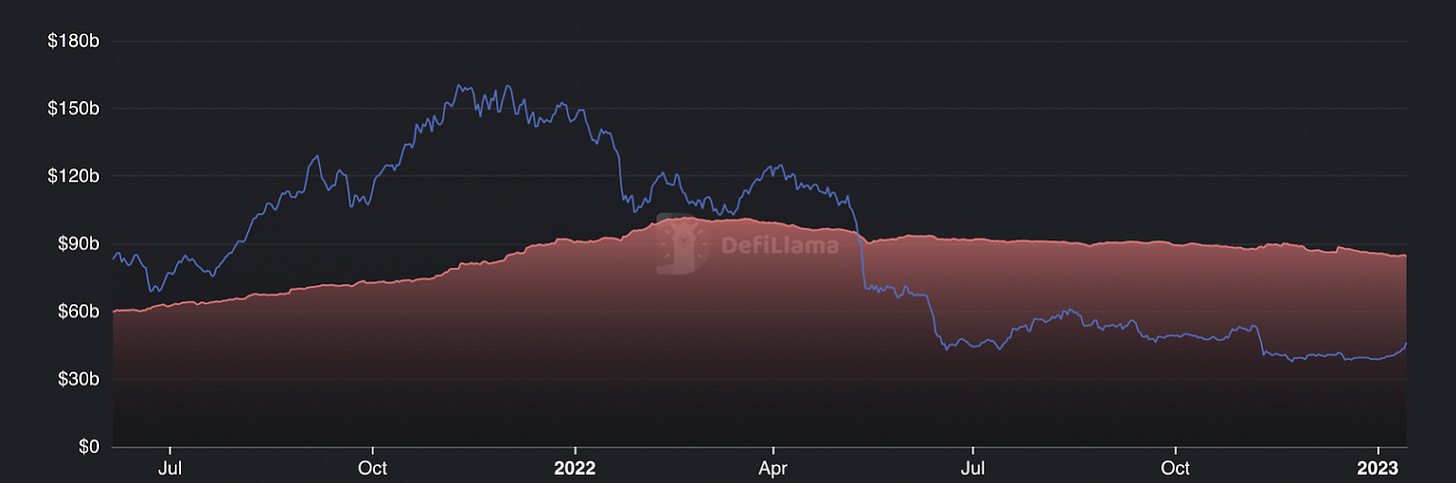
This measures the value of the stablecoins that are issued on and/or bridged to Ethereum. This decline can likely be attributed to redemptions of centralized stablecoins for fiat, as well as de-leveraging from borrowers using CDP based-stablecoins such as DAI and MIM.
Liquid staking deposits increased 105.1% from 3.4M to 7.0M
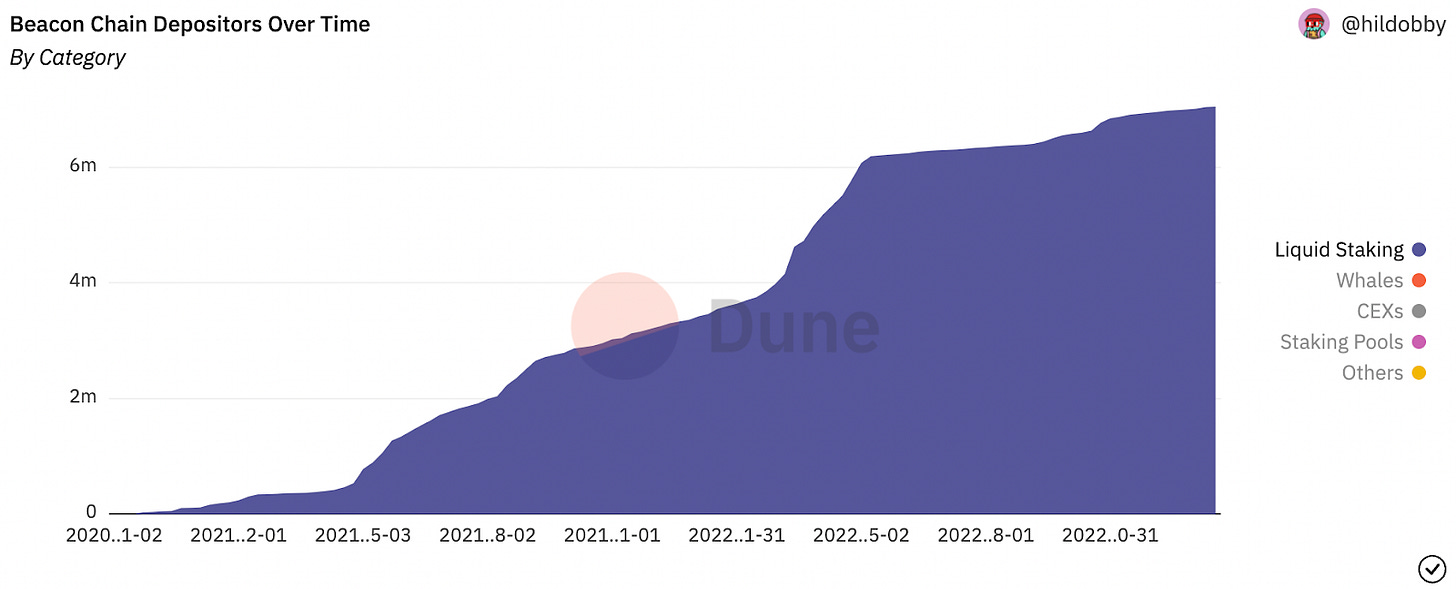
This measures the amount of ETH deposited into liquid staking protocols. This increase can be attributed to the broader growth in Ethereum staking deposits in anticipation of and following the Etheruem merge. This in turn has helped fuel growth in liquid staking protocols.
🎨 NFT Ecosystem
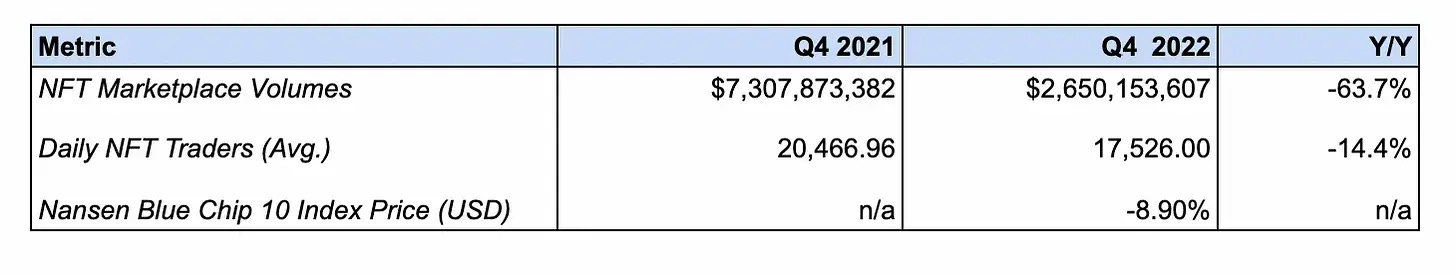
NFT marketplace trading volumes fell -63.7% from $7.3B to $2.6B
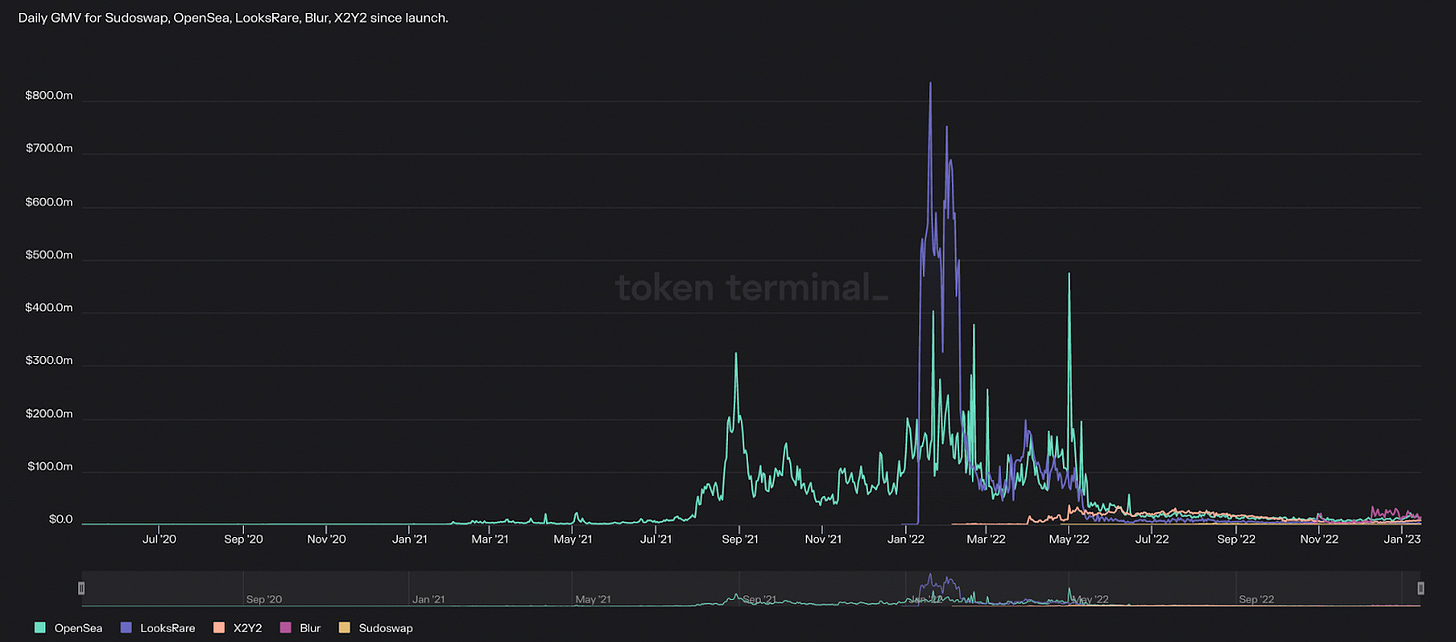
This decline can be attributed to weakness in both the broader crypto and NFT markets. Given that historically, trading volumes are positively correlated with prices, these price declines resulted in a decrease in speculative fervor and therefore trading activity.
The number of average daily NFT traders decreased -14.4% from 20,467 to 17,562
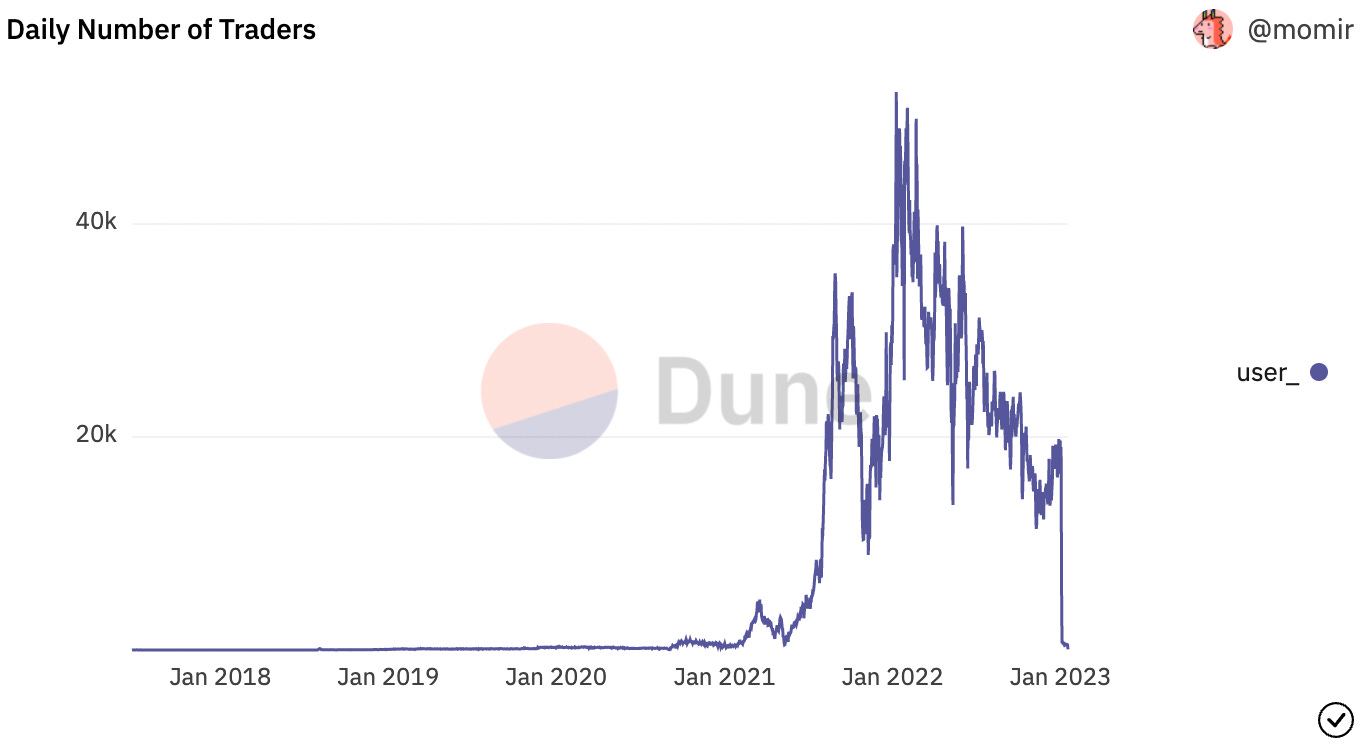
This decline is likely driven by the aforementioned slowdown in trading volumes, leading to less traders participating in the markets. However, the lesser decline in users relative to volumes is indicative of the stickiness of NFT trading.
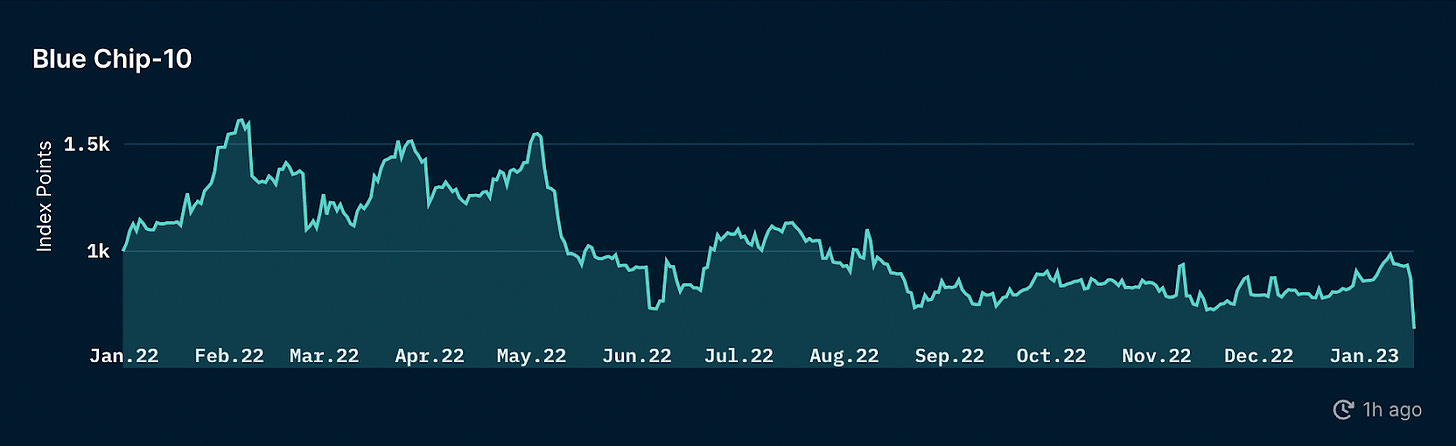
The Nansen Blue Chip-10 NFT Index fell -8.9% and -0.12% against USD and ETH respectively
This market-cap weighted index measures the floor price of ten large Ethereum NFT based collections, and its decline is likely due to the broader market sell-off during Q4 following the collapse of FTX.
🔗 Layer 2 Ecosystem
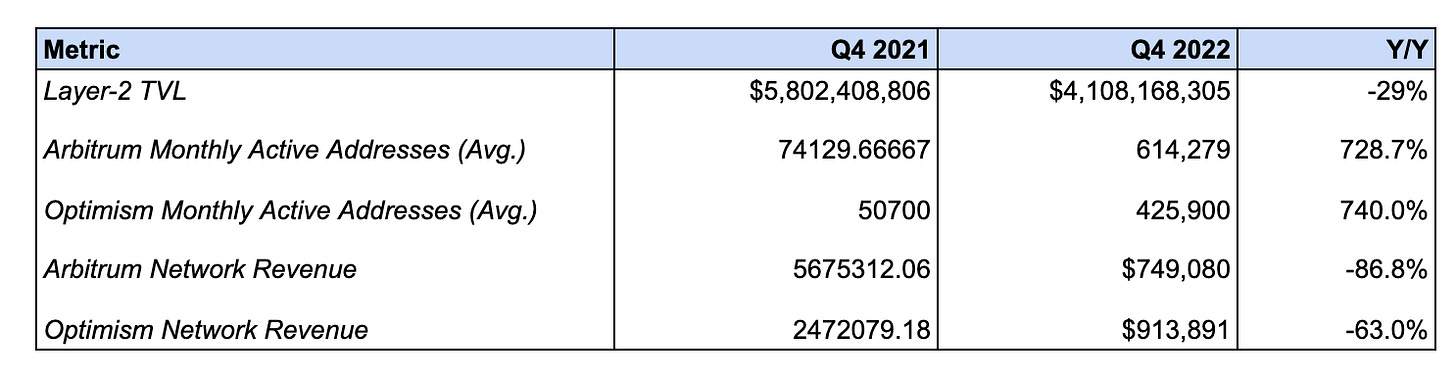
L2 TVL decreased -29.2% from $5.8B to $4.1B.
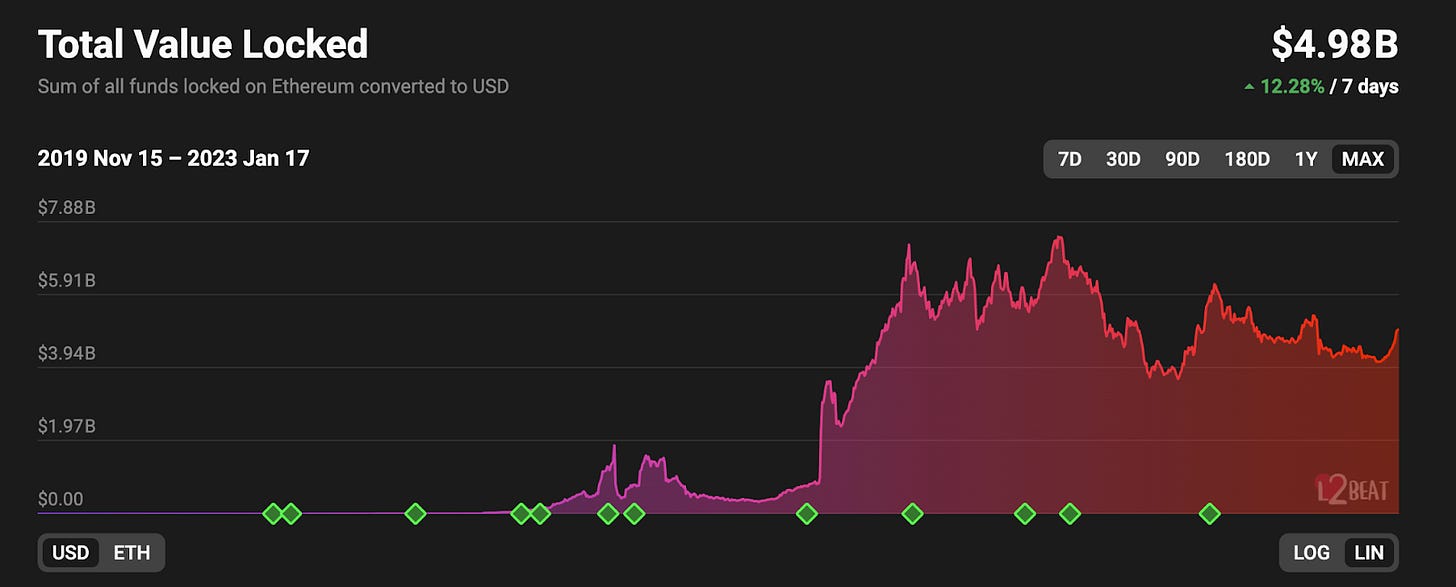
This measures the value of assets bridged to Ethereum L2s. As with L1 DeFi TVL, this decline can likely be attributed to a decrease in the price of ETH and other crypto assets, of which a significant portion of TVL is denominated. Given that ETH-denominated TVL rose 119.2% Y/Y, it’s likely that despite nominal declines, these networks saw net-inflows rather than outflows.
Arbitrum network revenue decreased -86.8% from $5.7M to $749K. Optimism network revenue fell -63.0% from $2.5M to $913K
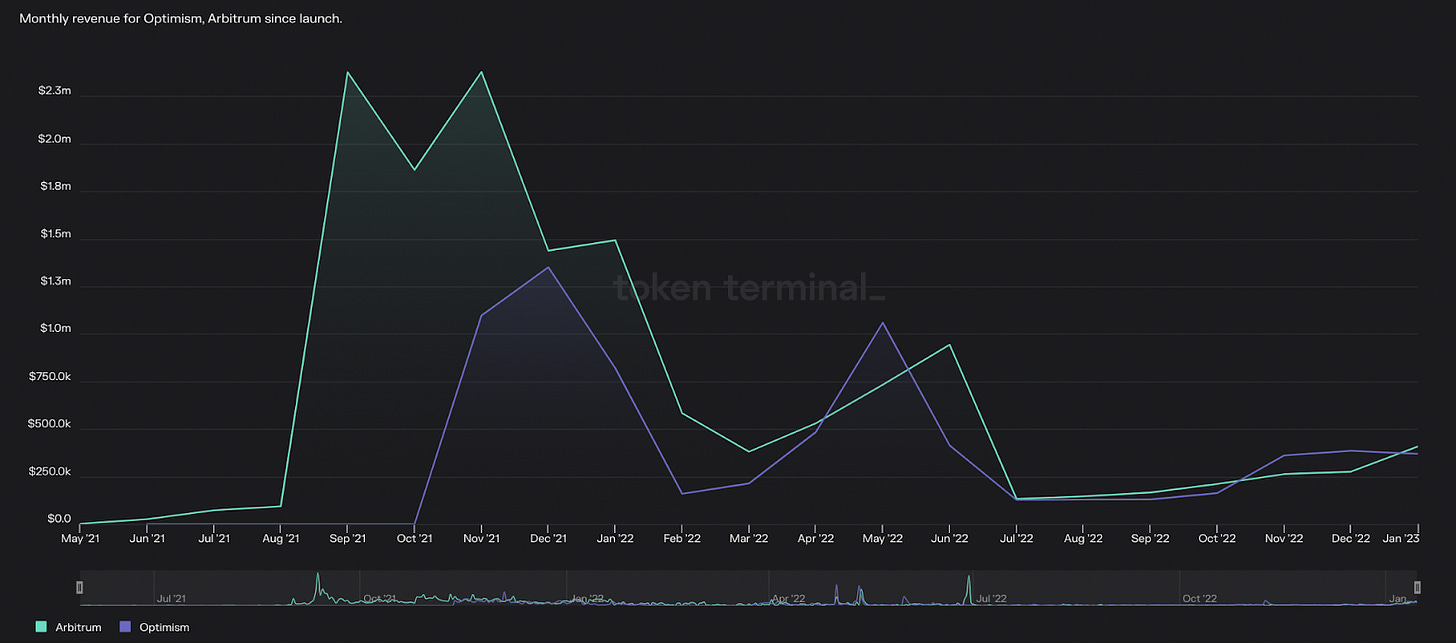
This measures the sequencer revenue earned by Arbitrum and Optimism respectively. This decline can be attributed to the broader decrease in blockspace demand as seen on Ethereum L1, as well as scalability upgrades such as Arbitrum Nitro which reduced gas consumption and transaction fees paid by end-users.
The average monthly active addresses for Arbitrum increased 728.7%. The average monthly active addresses for Optimism increased 740.0%.
This increase in address count can be attributed to the increased adoption of dapps on Arbitrum and Optimism. In the case of Optimism, this increased usage is likely also driven by the proliferation of OP incentive programs.
🌐 Ecosystem Highlights
Arbitrum and Optimism continue to grow
Along with the growth in the key KPIs discussed above, Q4 was filled with significant milestones for the Ethereum Layer 2 ecosystem.
One of the most notable of these is the “transaction flippening” in which Ethereum’s L2s collectively processed more transactions than L1. While this has briefly taken place at times in the past, L2s are now consistently processing more transactions than Ethereum itself since October 9, 2022. As of writing, rollups are processing more than 2.84x the transactions of L1, indicating that slowly but surely, Etheruem is continuing to scale.
L2s had numerous other milestones throughout Q4.
For example, Optimism launched “Quests,” which similar to Arbitrum Odyssey, is a campaign that rewards users for interacting with protocols on the network in exchange for earning NFTs. Quests have likely been a significant factor contributing to the growth of the network in Q4.
The quarter also showed the first signs of the OP Stack, Optimism’s development framework for creating interoperable, application-specific L2s, finding product-market-fit, as OPCraft, a Minecraft like-game, launched and captured the interest of the community.
Arbitrum also made noise in Q4 with the continued growth of decentralized perpetuals exchange GMX, who accounts for 38.4% of DeFi TVL on the network.
Catalyzed by the collapse of FTX, the DEX grew its trading volumes 14.2% Q/Q, while the GMX token is up 95.2% against USD and 29.1% against ETH respectively since the November ‘22 lows. Between more trading volume moving on-chain in the wake of the FTX implosion and the numerous projects such as Rage Trade, GMD, Umami Finance, and Dopex building on GLP, the future for Arbitrum, on-chain perpetuals, and DeFi as a whole seems bright.
PoS begins to take hold
Although the merge occurred towards the end of Q3, the effects of Ethereum’s long-awaited transition to PoS only began to took hold in Q4.
Along with a more than 99.9% decline in energy consumption, the most notable impact of the merge was the reduction in ETH emissions. As mentioned above, ETH was deflationary in Q4 despite the low levels of on-chain activity both before and after the immediate aftermath of FTX.
In a further testament to the effects of the merge, ETH became deflationary since the merge between November 8-30, as the market volatility during this period caused a significant spike in the gas fees, and in doing so the amount of ETH burned.
Furthermore, it’s likely that the reduction in sell-pressure post-merge, in particular the lack of miner capitulation, contributed to ETH not breaking the June lows during the FTX selloff, whereas other PoW assets like BTC made fresh lows.
Although we may be cheating a bit since this is supposed to be a Q4 report (I won’t tell if you won’t) Etheruem has since become deflationary again in the early days of Q1. It remains to be seen whether on-chain activity continues to increase, but should it, it is likely that ETH will remain deflationary and have reached its all-time peak supply on the day of the merge, September 14, 2022.
DeFi passes several stress tests
The onslaught of selling in Q2 following the implosion of Terra, Three Arrows Capital, and Celsius was a major stress test for DeFi, one which the ecosystem passed with flying colors as no major protocols accrued bad debt or became insolvent.
However, the ecosystem faced yet another challenge during and following the collapse of FTX and Alameda Research. In theory, the latter posed a particularly acute risk to DeFi, as Alameda was one of the metaverse’s largest yield farmers.
For instance, before the collapse of FTX more than 33% of the supply of the stablecoin MIM was backed by an FTT position held by Alameda.
Despite this seemingly major risk, DeFi proved resilient. Programmatic liquidation proved its mettle, as Alameda was forced to repay their debt before any other creditors, allowing MIM to avoid accruing bad debt. In addition, the market dislocation and illiquidity following the collapse of FTX led to other protocols being stress-tested.
For instance, in November Avraham Eisenberg attempted to leave Aave with bad debt of its own through shorting CRV, Curve’s native governance token. However the protocol’s risk parameters prevented a major incident, with Aave accruing just $1.6M in bad debt.
2022 stress-tested every organization, entity, and ecosystem in crypto. DeFi passed with flying colors, once again demonstrating its resiliency and antifragility while validating the proposition of an open, trust-minimized, autonomous financial system.
📅 Forward Outlook
There are numerous exciting catalysts for Ethereum heading into Q1.
The most significant of these is the highly anticipated Shanghai network upgrade, which is currently slated to go live in March. Shanghai will enable withdrawals from staking, and by fully de-risking staking, is poised to unleash a flood of inflows into liquid staking protocols over the coming months.
The L2 ecosystem is also set to see numerous exciting upgrades such as the launch of Bedrock, a major scalability upgrade for Optimism, as well as the possible resumption of Arbitrum Odyssey and the launch of the Arbitrum token.
DeFi is also set to see several key milestones, the most notable of which is the launch of Aave V3 on Ethereum L1. This upgrade, along with the launch of the protocol stablecoin, GHO, should help spur growth in Aave and perhaps renew interest in DeFi as a whole.
The NFT ecosystem is also set to experience a shake-up upon completion of the final Blur airdrop. Given that much of Blur’s usage has come in conjunction with its retroactive rewards program, it remains to be seen whether the marketplace will continue to maintain its market-share when the incentive program ends. NFT-Fi is another area to watch in Q1, with the growth of protocols like NFT Perp, a perpetual exchange for NFTs, and the launch of novel lending protocols like Asteria set to increase the capital efficiency of NFTs.
While there are a plethora of exciting protocol and application developments on the horizon, Ethereum faces several headwinds heading into Q1. This includes the continued fallout of the FTX collapse, including the possible bankruptcy of prime-brokerage Genesis, increased regulatory scrutiny for DeFi, as well as macroeconomic headwinds.
Ethereum is facing numerous challenges, but its future remains bright.
Results Tables
👨💻 Protocol
🏦 DeFi Ecosystem
🎨 NFT Ecosystem
🔗 L2 Ecosystem
About This Release
This release is not a release by Ethereum or the Ethereum Foundation.
About Ethereum
Ethereum is an open-source, decentralized blockchain network. Ethereum is a technology that’s home to digital money, global payments, and applications. The community has built a booming digital economy, bold new ways for creators to earn online, and so much more. It’s open to everyone, wherever you are in the world – all you need is the internet. (Taken from the Ethereum.org website)